 For the first time scientists have calculated the highest wet bulb temperature that humans can tolerate. We calculated wet bulb temperatures in a unit a couple months ago (it is equal to what is felt when wet skin is exposed to moving air and it includes the temperature and atmospheric huidity). Researchers discovered that if a human or animal is exposed to wet bulb temperatures above 95 degrees for at least six hours they will experience potentially lethal levels of heat stress. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimates that if the world continues warming at the same rate it is now, by 2100 average global temperatures will have risen by seven degrees Farenheit. The study has found that a warming of twelve degrees Farenheit would cause parts of the world to surpass the wet-bulb temperature limit, and that a warming of 21-degrees would place fifty percent of the globe in an unlivable environment. Researchers say that if nothing is done to slow global warming we may very well reach these temperatures, pretty scary!
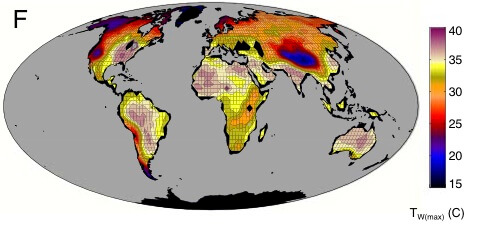
For the first time scientists have calculated the highest wet bulb temperature that humans can tolerate. We calculated wet bulb temperatures in a unit a couple months ago (it is equal to what is felt when wet skin is exposed to moving air and it includes the temperature and atmospheric huidity). Researchers discovered that if a human or animal is exposed to wet bulb temperatures above 95 degrees for at least six hours they will experience potentially lethal levels of heat stress. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimates that if the world continues warming at the same rate it is now, by 2100 average global temperatures will have risen by seven degrees Farenheit. The study has found that a warming of twelve degrees Farenheit would cause parts of the world to surpass the wet-bulb temperature limit, and that a warming of 21-degrees would place fifty percent of the globe in an unlivable environment. Researchers say that if nothing is done to slow global warming we may very well reach these temperatures, pretty scary! The map of the world shows the wet-bulb temperatures that would occur around the world with a global-mean temperature increase of 21 degrees farenheit. The white coloring portrays areas that humans would experienced potentially lethal heat stress.
No comments:
Post a Comment