1. Historical Eruptions
-Mt. Vesuvius: The Mt.Vesuvius eruption of 79AD was the most famous.
This is the one that destroyed pompeii and neighboring cities. Casualties wer
e estimated at about 10,000-25,000 people. Most died from pyroclastic flows that preserved remains of people. Famous for "plinian" eruptions. First documented account of eruption by Pliny the younger.

-Mt. St. Helens: Famous for 1980 eruption. Killed 57 people. Most destructive eruption in US history. The eruption was a VEI 5, or plinian eruption. The north face of the volcano collapsed causing it to erupt in that direction.
-Krakatau: Most famous for the 1883 eruption which was considered the largest in human history. It caused global temperatures to fall by 1.2 degrees celsius for about 5 years afterwards. It also darkened skies worldwide and in
spired the background for "Scream" a painting by Edward Munch.
2. Magma vs. Lava
-Magma is molten material under the Earth's surface and lava is magma that has breached the Earth's surface.
3. Parts of a Volcano
-Central Vent: Is an opening from which lava flows
-Magma Chamber: Is the source of molten materials that flow to the surface during an eruption
-Conduit/Fissure: Is a tunnel that connects vents to the magma reservoir
-Caldera: Is a bowl like depression at the top of a volcano. It can be created by either a collapse caused by an empty magma reservoir or by the volcano blowing it's top off.
-Crater: Is a bowl-shaped geological feature at the top of a volcano.
4. Identifying and describing volcanoes
-Shield: formed by effusive eruptions of fluid, mafic lava. Form at the ocean floor over hot spots. have a gently sloping shape. Look like a big hill.
-Cinder Cones: Circular cone shape. Built from particles and blobs of congealed lava being ejected from a single vent. As the lava is blown into the air it breaks into small fragments and settles on the sides of the volcano causing it's shape.
-Stratovolcanoes/Composite: Has the classic volcano shape. Built from effusive eruptions that spew layers of tephra and felsic lava that settle on the sides of the volcano. They continue growing until the slope exceeds the threshold of stability and then it collapses.
-Calderas: Formed when magma is removed and the top of the volcano collapses forming a caldera. They are the largest and most explosive forms of volcanoes and contain lots of magma.
5. How Volcanoes Form
-Pacific Ring of Fire: The pacific ring of fire is along the subducting boundaries of the Pacific plate. Subduction volcanoes dominate this area.
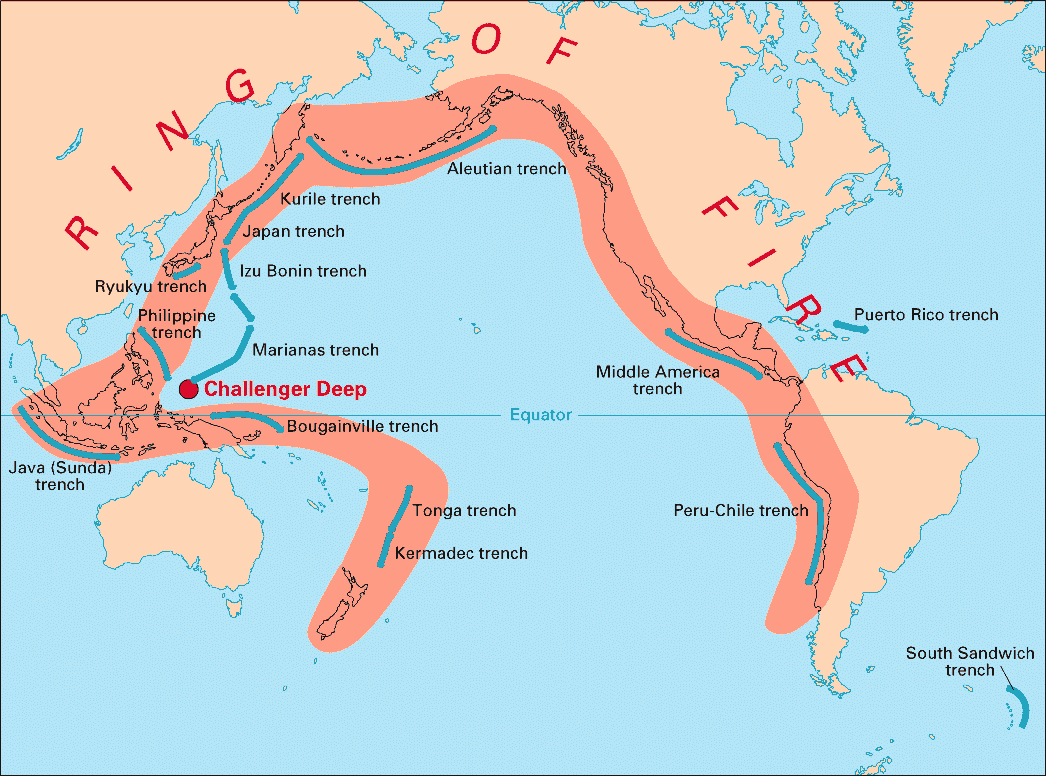
-Subduction Volcanoes: Form when an oceanic plate goes under a continental plate. Examples are... Cascade range & Andes Mountains.
-Volcanic Island arcs: Form when an ocean plate goes under another lighter oceanic plate. Examples are... Japan, New Guinea & Aleutian Islands.
-Rift/Divergent Boundaries: form when two plates diverge. Hydrothermal vents form at mid ocean ridges and the magma heats the water to 400 degrees. Examples are... Great Rift Valley.
-Hot Spots: form over hot spots. Examples are... Hawaiian Islands, and Canary Islands.
No comments:
Post a Comment